Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, has traditionally been treated through surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Now, radiation oncologists are playing a pivotal role in reshaping the treatment landscape.
Using high-precision technologies and individualised care strategies, radiation specialists are extending life expectancy and improving quality of life. Let’s explore how this transformation is unfolding in clinics worldwide.
Why Melanoma Requires Advanced Treatment Approaches
Melanoma is aggressive. It spreads quickly, often to the brain, lungs, or liver, making early and effective intervention critical.
Traditional treatments have limitations. Surgery isn’t always an option, especially for inoperable tumours or metastatic disease. Best Radiation Oncologist in Gurugram Chemotherapy's side effects and variable success rates make it less ideal for some patients.
This is where radiation oncology steps in. Modern radiation treatments can precisely target tumours without harming surrounding tissue, which is crucial for sensitive areas like the brain or spine.
Radiation is now a primary tool, not just a backup. It’s used for brain metastases, local control of primary tumours, and even in conjunction with immunotherapy to increase efficacy.
More institutions are adopting this integrative approach, and the results speak volumes—better tumour control, fewer side effects, and improved survival in many cases.
The Role of Radiation Oncologists in Melanoma Care
Radiation oncologists do more than operate machines. They develop treatment plans tailored to each patient’s tumour type, size, and location.
They collaborate with dermatologists, surgeons, and medical oncologists to provide coordinated care. This team-based approach ensures optimal outcomes across different stages of melanoma.
Radiation oncologists bring imaging data, pathology reports, and clinical history into every planning session. This allows them to determine the ideal dose and delivery method, maximising impact while reducing harm.
They also play a key role in follow-up, monitoring response, adjusting treatment if needed, and managing side effects. It’s a continuous, data-driven process designed to provide patients the best shot at remission or control.
Personalised Radiation Planning
Every tumour is different. That’s why personalised treatment is essential.
Radiation oncologists use CT, MRI, and PET scans to map tumour margins. They customise radiation angles, intensity, and duration based on these images and the tumour’s biology.
This approach increases accuracy and decreases exposure to healthy tissue. It also lowers the risk of complications like fatigue, skin changes, or neurological issues.
Precision isn’t a luxury—it’s a necessity in melanoma care, especially for brain or spinal lesions.
Advanced Technologies: SRS and IMRT
Two technologies stand out: Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT).
SRS delivers concentrated radiation to brain metastases in one or a few sessions. It spares the rest of the brain, reducing cognitive side effects.
IMRT shapes radiation beams to match the tumour’s shape. This allows higher doses where needed and protects nearby organs.
Both have proven effective in improving control rates and reducing toxicity in melanoma patients.
Combining Radiation with Immunotherapy
Radiation is no longer a standalone tool. It’s being used alongside immunotherapy to unlock powerful synergies.
This combination can enhance the body’s immune response to cancer. Radiation damages tumour cells, exposing antigens that immunotherapies can then target more effectively.
This technique, known as the abscopal effect, has shown promise in spreading immune activation beyond the irradiated site.
More trials are underway, and early results show increased tumour regression and longer survival in some patients.
This represents a major leap in systemic melanoma treatment.
FAQs
Q 1: Is radiation therapy safe for melanoma patients?
A 1: Yes, especially with newer techniques like IMRT and SRS, which minimise side effects.
Q 2: When is radiation used for melanoma?
A 2: Commonly for brain metastases, inoperable tumours, or as an adjunct to immunotherapy.
Q 3: How long does radiation treatment take?
A 3: Sessions can range from one to five for SRS, and several weeks for other types.
Q 4: Can radiation cure melanoma?
A 4: While not always curative, it can significantly control tumour growth and improve quality of life.
Conclusion:
Radiation oncologists are redefining how we treat melanoma. With targeted planning, advanced tools, and combination therapies, they offer hope where few options once existed. Patients now benefit from personalised care, fewer side effects, and better outcomes. Best Radiation Oncologist in Gurugram is more than progress—it’s a shift in how we fight one of the most dangerous skin cancers.

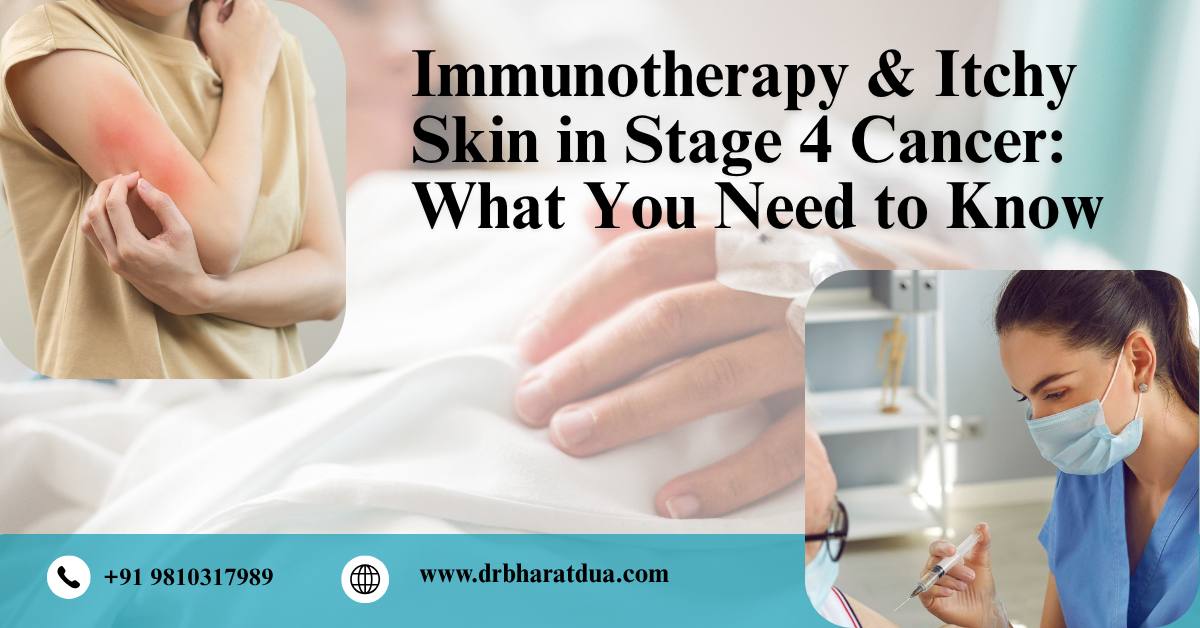 Learn how immunotherapy can cause itchy skin in stage 4 cancer patients. Dr. Bharat Dua, the Best Radiation Oncologist in Gurugram, shares insights, and care tips.
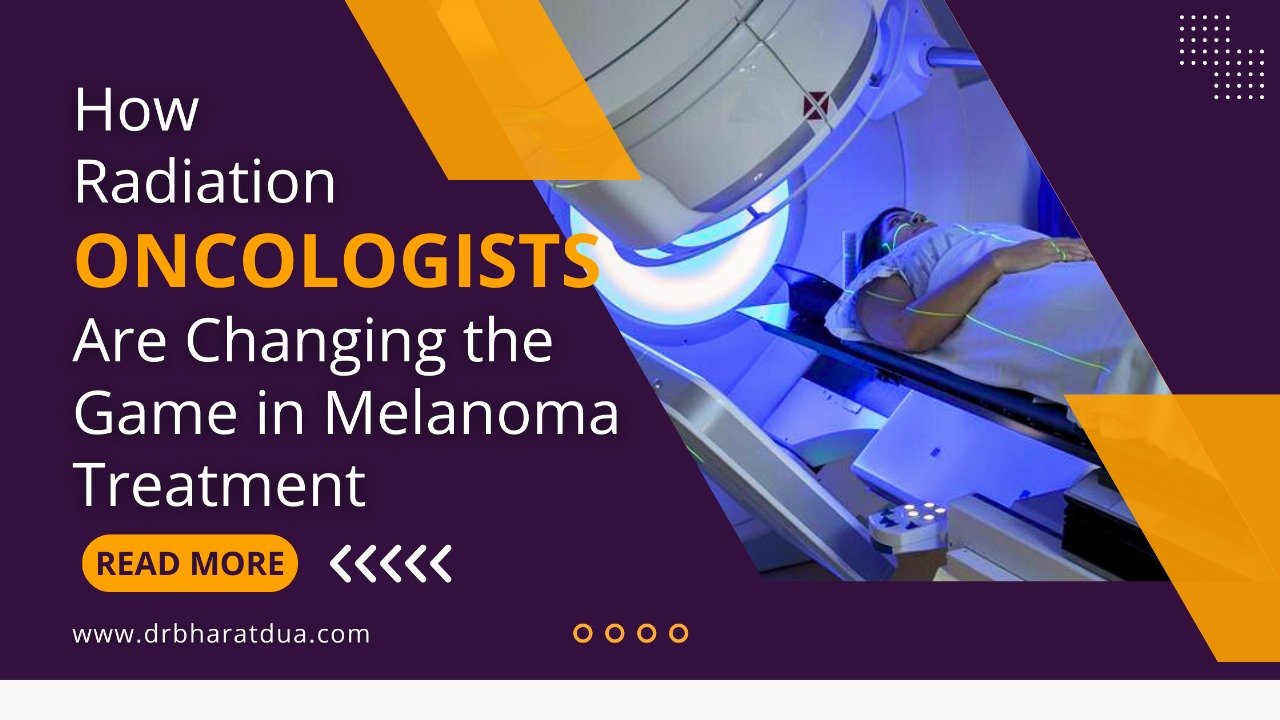
Learn how immunotherapy can cause itchy skin in stage 4 cancer patients. Dr. Bharat Dua, the Best Radiation Oncologist in Gurugram, shares insights, and care tips..png) Modern radiation oncology targets tumors with precision while protecting healthy tissue with the Best radiation oncologist in Gurugram.
Modern radiation oncology targets tumors with precision while protecting healthy tissue with the Best radiation oncologist in Gurugram.